
Medically Reviewed by Annamarie Coy, BA, ICPR, MATS
In this article
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a pattern of alcohol use that occurs when a person:
Those with AUD also develop a high tolerance to alcohol and withdrawal symptoms after stopping drinking.
Alcohol dependence is a growing problem worldwide. According to a 2023 study by the National Center for Drug Abuse Statistics, 10% of people over 12 in the United States have an AUD.1
When it comes to substance abuse, every person is different. Some people become addicted to alcohol over time, while others are biologically prone to alcoholism.
Common causes of alcoholism include:
According to the NIAAA, genetic factors account for about 50% of people developing an AUD.2 Genetic factors and a family history of alcoholism can contribute to your risk of developing AUD.
There isn't just one "alcoholic gene" that increases a person's risk of developing alcoholism. Studies show that AUD is a complex genetic disease.
Hundreds of genes can impact the risk. However, certain gene combinations can make you more susceptible.
Two genes that have the most vital known link to alcoholism include:
Certain gene variations, such as the beta-klotho gene, decrease your risk of developing alcoholism. People who don't have the beta-klotho gene may find it difficult to have just one or two drinks.
AUD may often co-occur with a mental illness (dual diagnosis), including:
People with other mental health conditions often drink alcohol to relieve unpleasant symptoms.
A person’s poor coping skills regarding stress, negative feelings, and boredom can make them vulnerable to alcohol addiction. If they cannot handle stressors, alcohol can make dealing with it easier.
Some people also believe alcohol controls their mental health symptoms better than medications. However, using alcohol as a "crutch" to ease symptoms increases the risk of alcoholism.
Even without a genetic component, you can still develop alcoholism when raised or immersed in a specific environment. Growing up around people with addiction predisposes someone to develop an AUD.5
Alcoholism can also develop in people who drink in social situations, such as college students. Binge drinking, which is common amongst college students, is a harmful drinking pattern that makes someone’s blood alcohol concentration (BAC) level rise to 0.08% or higher. While binge drinking in college may seem ordinary, it can lead to lasting AUD.
Some risk factors associated with alcohol addiction include:6
Drinking from an early age increases the risk of developing an AUD later in life.
Environmental factors, like pressure from friends, family, and media, can contribute to excessive alcohol consumption and addiction. The media portrays alcohol as a way to wind down or deal with stress, encouraging people to drink.
High stress levels increase your risk of addiction. Whether your stress comes from your job, finances, or relationships, finding healthy coping mechanisms is essential to reduce the risk of turning to alcohol.
Genetics plays a prominent role in problem drinking. Genetic mental illnesses also increase your likelihood of developing an addiction.
A history of emotional or physical trauma can increase the risk of AUD.
Alcohol can be a method of self-medication for those with mental health conditions, potentially leading to alcohol addiction.
AUD affects men more than women. Women’s bodies absorb more alcohol and reach a higher BAC even after drinking the same amount.
When you engage in frequent alcohol consumption, your body develops a tolerance, and a dependence forms over time. Because of this tolerance, your body needs more alcohol to feel the same effects.
Drinking alcohol in moderation can be harmless, but over time, it can develop into abuse or addiction.
The symptoms of alcoholism vary and can range from mild to severe.
The most common signs of alcohol use disorder include:7
AUD typically involves alternating periods of alcohol intoxication and withdrawal symptoms.
Alcohol withdrawal can occur when alcohol use has been heavy and prolonged but suddenly stopped or significantly reduced. It can occur within several hours to 4 to 5 days later.
Signs and symptoms of alcohol withdrawal include:
Alcohol depresses your central nervous system (CNS), affecting your speech, muscle coordination, and brain health. Heavy drinking can even cause many life-threatening impacts on your safety and health.
Drinking excessive alcohol can reduce your judgment skills and lower your inhibitions. These lapses can lead to poor decision-making and dangerous situations or behaviors, including:
Consuming too much alcohol, either on a single occasion or over time, can lead to serious health issues, including:
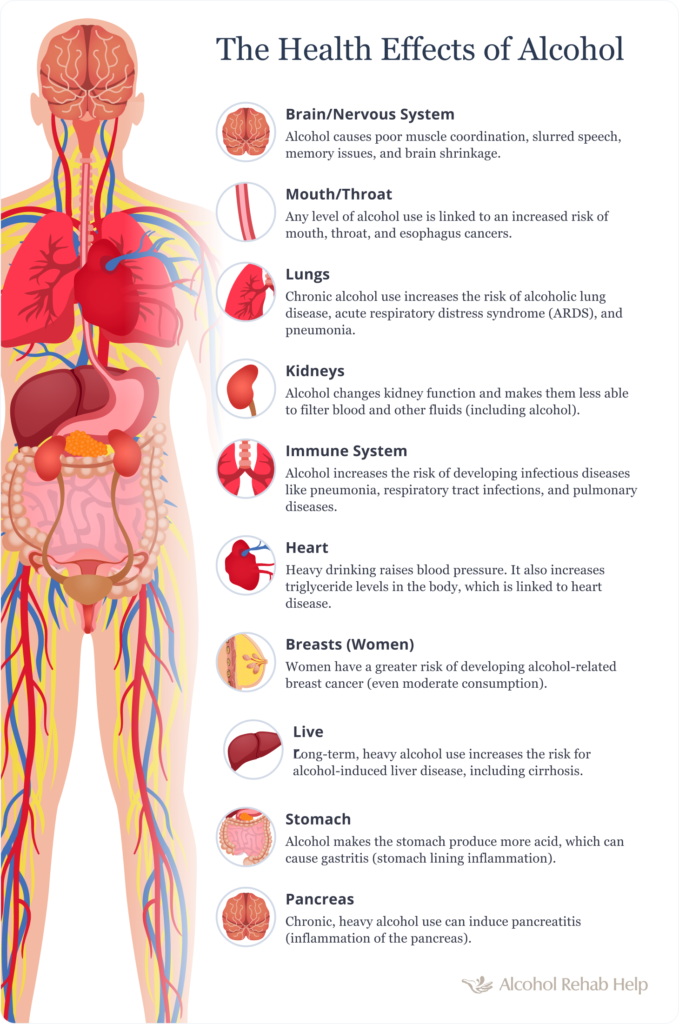
The graphic displays only some health issues that heavy drinkers may develop. It is essential for anyone struggling with alcoholism to seek medical care to avoid serious health complications.
If you or a loved one struggles with AUD, help is available. Standard treatment options for AUD include:8
Inpatient treatment is an effective option for alcohol use disorder (AUD). This type of treatment takes place at a licensed residential treatment center.
Patients receive 24-hour comprehensive and structured care. They also undergo medical detox, including medication-assisted treatment (MAT).
Outpatient treatment helps people with less severe alcohol use disorders. It works around a person's schedule and does not provide 24-hour medical supervision.
Support groups act as emotional support systems for people fighting AUD. In support groups for alcoholics, a person in recovery can relate to others with the same condition. Peers can positively help each other remain sober.
Early treatment is critical. While AUD can range from mild to severe, even a mild disorder can lead to serious health issues.
If you feel that you tend to drink too much alcohol, your drinking is causing problems, or your loved ones are concerned about your drinking, reach out to your healthcare provider.
You may not recognize how much you drink or understand the connection between alcohol use and the problems in your life. Listen to your loved ones when they ask you to examine your drinking habits or seek help.
You may benefit from a rehabilitation program, a support group such as Alcoholics Anonymous, or a self-help group.
Alcohol use disorder is characterized by excessive drinking, an inability to control alcohol consumption, and continued drinking despite the negative impacts of alcohol abuse on one’s life.
Biological, psychological, and social factors can trigger an AUD. Certain risk factors, such as a family history of alcohol addiction or high stress levels, put somebody at a higher risk for developing AUD.
Despite all the adverse effects of AUD, help is still available. There are various options for treatment, like inpatient and outpatient programs and support groups.
In this article
